HADEF Chahida
Oran 2
Summary :
Globalization has today become a major sort of debate among the world. Its impact is profound .In this era, the world of education in general and that of languages in particular knows a deep reform and evolution, in order to face up the new challenges, education has to adapt and renew itself. The introduction and application of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) is a noticeable change which has invaded foreign language departments under the reform of the curriculum. In this paper, we have investigated the main changes, effects, factors, challenges and problems that EFL knew in the globalization era and which are mainly associated with the integration of technologies in EFL teaching and learning in the case of Algerian educational level with special focus on teachers and students.
Key words: information, communication, technology, languages, teaching, learning.
Résumé :
La mondialisation est devenue aujourd’hui un débat majeur dans le monde. Son impact est profond. Le monde de l’éducation en général et celui des langues en particulier connaît des réformes profondes, afin de faire face aux défis de la globalisation. L’introduction et l’application des technologies de l’information et de la communication (TIC) sont devenus une nécessité absolue. Cet article traite les principaux changements, les effets, les facteurs, les défis et les problèmes relatifs à l’enseignement des langues étrangères en mettant l’accent sur les enseignants et les étudiants à de l’Université algérienne
Les mots clés : Information, communication, technologie, langues, enseignement, apprentissage.
Introduction
The world of education in general and that of languages in particular is in constant evolution in order to face up to the upheaval and professional levels. Therefore, education has to adapt and renew itself to be compatible with the globalised society.
The new era assigns new challenges and bests on the modern teacher. Thus, the tradition of language teaching has been drastically changed with the remarkable entry of the information and communication technologies (ICTs).
The integration of ICT in teaching and learning foreign languages is not a method. Rather, it is a medium in which various methods, approaches and pedagogical philosophies may be implemented in order to convey the desired outcome. Consequently, the effectiveness of ICTs depends on how and why it is applied and for what.
So, the problematic arising here is ‘How can ICT be used to support foreign language teaching and/or learning, and what are the main challenges that face its integration in educational settings’?
Part One: The Use of ICT in teaching and learning Foreign Languages
1.1. History and Definition
ICT is the common abbreviation for ‘Information and Communication Technology’. Thus, it is the technology required for information processing, in particular, the use of electronic computers, communication devices and software applications to convert, store, protect, process, transmit and retrieve information from anywhere at anytime This abbreviation is built on three essential terms : Information : refers to the knowledge obtained from reading, investigation, study or research. Communication is an act of transmitting messages using either verbal or non verbal language while technology is the use of tools based on scientific knowledge, experience and resources to create processes and products that fulfill human needs, Perron, et.al. (2010:67) define it as:’’ Technologies used to convey, manipulate and store data by electronic means’’
1.2. Effective ICT’s Equipment and Service
ICT acts as a tutee when learners use them in order to gain more understanding and learn new knowledge. A number of different ICT tools and applications may be integrated in teaching and learning [8]. Some of these tools and applications may be designed specifically for educational purposes and some others for more general use. The choice of resources, and the way they are used can be linked to different learning theories namely.
The most useful ICT services would be:
1.2.1-Video Conferencing : is one of the most interesting technology which is used to present data , lessons, researches to a great part of audience ,according to Heath and Holznagel (2002 :4) “As we move into the new century, advances in technology communication systems provide more sophisticated educational opportunities for content delivery across video conferencing is a communication means used for lectures, tutorials, workshop, project review, remote site visit etc instances to reach wider audiences.”
So, video conferencing has facilitated the teacher/instructor to transfer data and knowledge to wider range of learners since it provides a specific learning environment where learning is integrated with entertainment. In this atmosphere, the teacher plays the role of a facilitator consequently, hems ay enhance learners’ attitude and motivation.
1.2.2-Computer-Assisted Language Learning ‘CALL’: Offers a wide range of ICTs’ applications that notably increase learners motivation. CALL has come to encompass issues of materials design, technologies, pedagogical theories and modes of instruction.
Materials for CALL can include those, which are purpose-made for language learning, and those, which adapt existing computer-based materials, video and other materials (Beatty, 2003, pp. 7-8).
Types of CALL Activities
|
– multiple-choice & true/false quizzes – gap-filling exercise/cloze – matching – re-ordering/sequencing – crossword puzzles – games – simulations |
– writing & word-processing – concordancing – web quests/searching – web publishing – online communication (synchronous and asynchronous)
|
1.3. Approaches to Learn Languages:
The integration of Technologies in educational institutions gave birth to three different approaches. Support to traditional instructions which consider lesson planning crucial when using ICTs. However, introducing technology alone will not change the teaching and learning processes. ICTs can enable teachers transform their teacher practices given a set of enabling conditions.
So, ICTs are seen as tools to help teachers create more ‚learner-centric‘ learning environments since teacher can challenge pupils’ understanding and thinking, either through whole-class discussions and individual/small group work using ICTs. ICTs are seen as important tools to enable and support the move from traditional ‚teacher-centric‘ teaching styles to more ‚learner-centric‘ methods. Furthermore, they can be used to support existing teaching practices. Blended Learning is also the most effective approach since it combines the advantages of both traditional instruction and e-learning (Horton 2000). It is known, also, as hybrid instruction combining the strengths of classroom techniques with those of web-based training. (Gardham and Kaleta, 2002).
The third one is E-Learning defined by Derek Stockley (20003 :101) as : “ The delivery of a learning, training or education program by electronic means.”
1.4. ICT in Teaching and Learning Languages:
The 21st century is the age of Globalization in which according to
Graddol (1997:16) ‘Technology lies at the heart of the globalization process, affecting education work and culture.’
The integration of ICTs brought set changes in the field of teaching / learning foreign language among which
-
Expanding Access to education through ICT
-
Promoting Efficiency of Language Teaching
-
Promoting Student-Centered Curricula
-
Improving the Quality of Learning
-
Learning Time vs. Classroom Time
-
Motivating to Learn
-
Fostering Inquiry and Exploration
-
The Changing Roles of Language Teachers
-
ICT as a Foreign Language Teaching Support
-
ICT and the Teaching of ESP
-
Authentic Resources Used in ESP Learning
-
The impact of ICT Tools Used in Learning ESP
1.4.1. Technological Learning Environment:
With The entry of technological material in the educational settings, there was a need for organizational change for both teacher and learner within a fully different environment. The following diagram represent an organized plan for a digital learner and show the change of teacher’s role, learner learning atmosphere and the impact of ICTs on them :
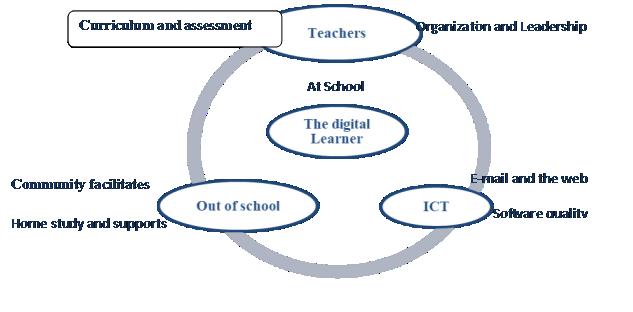
Diagram 1: An organized plan for a digital learner (OFCD 2001)
1.4.2 Benefits of ICT
In order to explain or predict learning benefits from the use of ICT. Roblyer and Edwards believe that the use of ICT in education has evolved from two main approaches, namely directed and constructivist instructional methods. The theoretical foundations of directed instruction are based on behaviorist learning theories and information processing theory, which is a branch of cognitive psychology. The theoretical foundations of the constructivist approaches are based on the principles of learning derived from cognitive learning theory.
Information and communication technology ‘ICT’ has specific advantages which can revolutionize the educational field. For Newman (2002) and Wheeler (2000) argue that the benefits include:
- shared learning resources and learning spaces
- The promotion of collaborative learning and the move towards autonomous learning
- ICT has the potential of enabling students and teachers to use video systems to transmit television programs and information
- It has the potential of minimizing costs and improving the quality of teaching and learning
Networks facilitate learners communication.
- It helps student to access, manipulate, modify, store and retrieve information
- It enables children to exert more choice over how they approach study, requiring less direction from teachers.
- The teacher’s role will become more and more “a guide or moderator rather than as a director” (Forsyth, 1996:31).
- ICT enhances educational reform
- It helps language teachers and learners language to deal with language items, pronunciation and lexis
- Make learning more enjoyable
- Provide extra- socio-economic and pedagogic benefits in society.
Part Two ICT’s In the Algerian Educational Setting: Challenges and Bets.
The role of ICT in foreign languages’ teaching and learning is becoming more and more important and its development will be continued through distance learning. Algeria, as an example, is encouraging and promoting the use of ICT to improve the development process in general and the educational system in particular.
2.1. Challenges
Any new process would be implemented for a range of disciplines using certain material surely face problems and come about obstacles ,these latter may complicates or even stop the flow of the innovative process.
The most noticeable challenges which face the integration of ‘ ICT’ in teaching and Learning Languages as stated by Korte & Husing, 2007 :
- lack of teacher confidence, competence and effective training,
- The resistance to change and negative attitudes,
- lack of technical support and lack of infrastructure
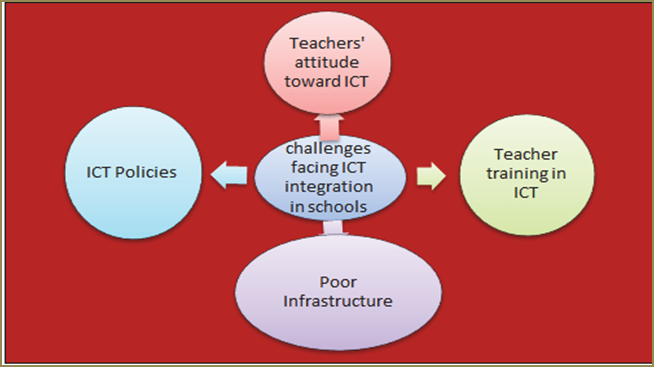
Fig: 2.1: Factors that affect the integration of ICT
Sources: Adapted from Korte & Husing, 2007
2.2. ICT in the Algerian Education (Policies):
The Algerian government gives the ministry of post and information technology the responsibility of implementing and managing the national ICT policy.
At the same time the government has also initiated collaboration with a number of worldwide agencies to develop the ICT standing in the country.
In 2003, the country launched a program to ensure access to ICT through making computers available for every home initiative
In order to facilitate the entry of Algeria into the information society, the following national ICT initiatives have been designed:
- The project of the Ministry of Education to equip all schools with computers by 2005.
- The distance Education Project.
- The Virtual University Project
- The research network to be put in place by the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research.
- The health network developed and maintained by the National Health Development Agency (ANDS).
- The Djaweb Internet platform.
2.3. The Integration of ICT in Teaching Languages in Algeria (case of students in the department of foreign languages):
A survey was conducted in the department of foreign languages with 30 students whose age ranges between 18-22 years old and 4 university teachers to assess the application of ICTs in the teaching and learning process.
2.3.1-Learners’ Learning Strategies:
We have asked them about their learning strategies .The following pie-chart shows the findings as regards the effectiveness of ICTs on foreign language students.
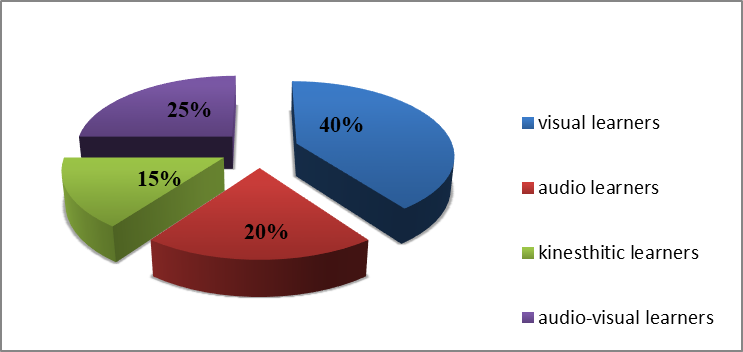
Figure 2.2 EFL Learners learning strategies
The results show that the majority of students seem to be visual learners which means that they learn more with the use of visual aids such as: datashow, video conferencing, television….
2.3.2. Media used in Teacher-Learner Communication:
Many social media and networks have appeared. Surprisingly, all the teachers maintained that they used different browsers to communicate, guide, help and improve their students’ level.
The following table shows the media used by the teachers:
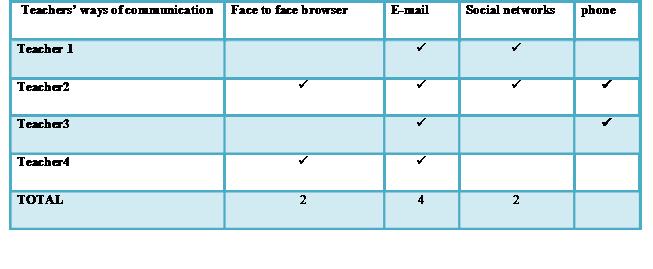
Table 2.1 :Media used in teacher-learner communication
So , it is clearly shown that language teachers hold positive attitudes towards the use of ICTs in improving their students’ level, in addition , we notice that they use different electronic media to do so
2.3.3 The Use of ICT’s as Learning and Teaching support:
Learners and teachers were asked to show off their point of view towards the use of ICTs in educational settings:
Foreign Language Learners argued that they :
- Enjoy Learning using ICT’s
- Practice the language in World Wide Communication
- 100% of them get Knowledge and data from the internet sources.
- Understand more while watching educational videos, slideshares, powerpoint presentation and so on.
- Appreciate lesson presented by data show.
- Technological materials such as phones lab-tops facilitate sharing information.
However,
Teachers’ Attitudes :
- University don’t have enough material
- No available equipped rooms and labs for using video conferencing.
- No real internet flow
- Some learners do not have access to social netwoks and have no e-mail accounts
- Some students use ICT’s to have fun
- The huge number of students is a real obstacle
2.4. Recommandations:
After the investigation, the researcher came up with some proposals that may be used in order to wisely integrate ICT in education .So University/school have to:
- Prepare to a digital society
- Develop a policy based on its own vision
- Make use of more digital tools
- Provide sufficient material
- Provide an academic training for teachers on how to use ICT’s in teaching.
- Prepare an equipped rooms
- Use video Conferences to present lectures
Conclusion:
The sharp rise in the application of information and communication technology ICT resources in the curriculum has been driven to a large extent by the adoption of interactive pedagogy and related technologies in classrooms. However, the combination of technology into education seems reasonably doubtful if it is not integrated carefully and wisely.
It should be acknowledged that technology brought benefits and challenges to the educational field especially for foreign languages teaching and learning. Therefore, the teaching principle have to appreciate the new technologies, which provide things decisively new, and useful however, teacher should never let machines take his role.
References:
Algeria: The United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA) http://www.uneca.org/aisi/nici/Algeria/algeria.htm
Bell, D.(1973).The Coming of Post –Industrial Society.New York : Semiotext(e).
Korte, W. B., & Husing, T. (2007). Benchmarking access and use of ICT in European schools 2006: Results from Head teacher and a classroom surveys in 27 European countries, elearning papers, vol. 29, no. 10, pp. 1-6.
Newman, P. (2002) Exploring discussion lists: steps and directions. In the Proceedings of Joint Conference of Digital Libraries, Portland, Oregon. Available from [Accessed 20th of April, 2011]
Perron, B. E., Taylor, H.E., Glass, J.E. & Margerum-Leys, J. 2010. Information and Communication Technologies in Social Work. Advances in Social Work, vol. 11, No. 1 (Spring 2010), pp. 67-81.
Study in Algerian Education System. Arabian Campus available at: http://www.arabiancampus.com/studyinalgeria/edusys.htm
Wheeler, S., (2000) The Role of the Teacher in the use of ICT
Wiener, N.(1956). The Human Use of Human Beings: Cybernetics and Society. New York: Doubleday & Company Inc.
